All but Which of the Following Are Post-transcriptional
MiRNAs tRNAs and rRNAs all _____________. B act in the nucleus.
Post Transcriptional Modifications Rna Processing Concise Medical Knowledge
Which of the following is an example of a post-transcriptional modifications select all correct answers.

. A Addition of 7-methylguanosine triphosphate cap. C are packaged with other proteins to form RISC. RNA Splicing the First Stage of Post-transcriptional Control.
All of the above. RNA polymerases II produces hnRNA heterogeneous nuclear RNA which is. A do not code for proteins.
All of the following statements about post-transcriptional processing of tRNA are true except. Chapter 16 Problem 15RQ. Tailing refers to cleavage of 3 end and the addition of 80 to 250 A residues to create a polyA tail.
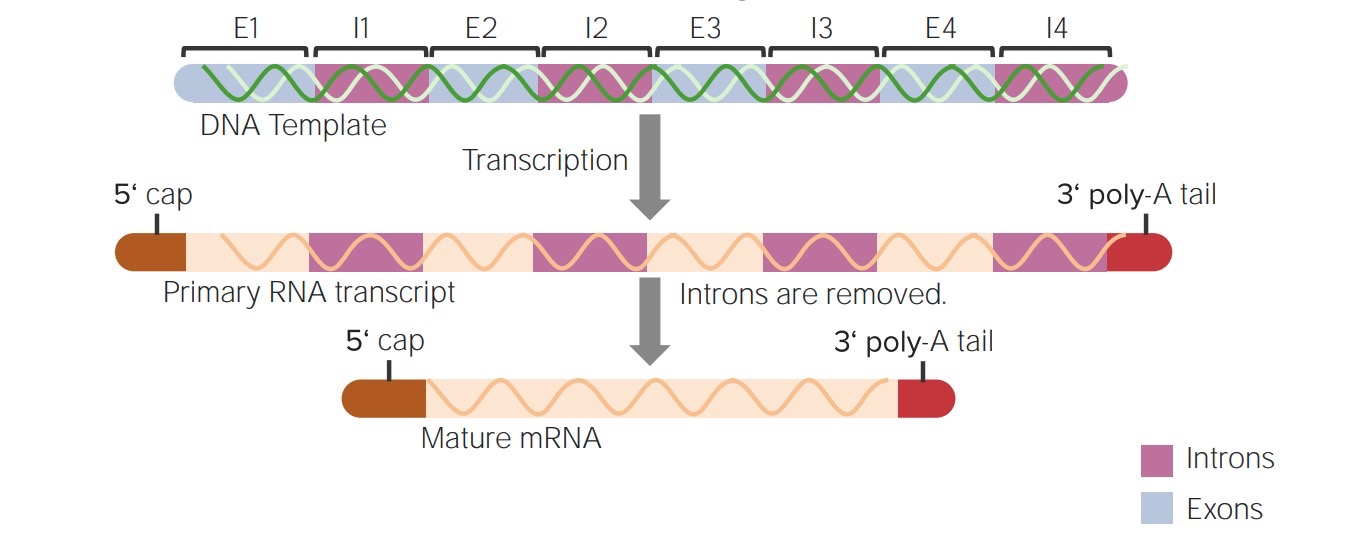
Which of the following isare post-transcriptional modifications occurring in eukaryotic mRNAs. In this step poly A tail is added to 3 end of RNA. These modifications are called post-transcriptional modifications.
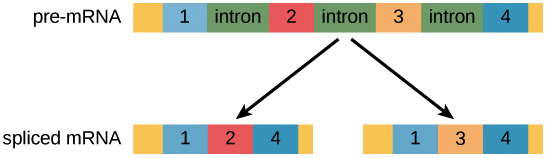
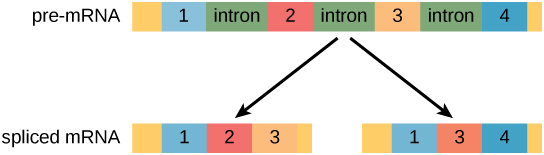
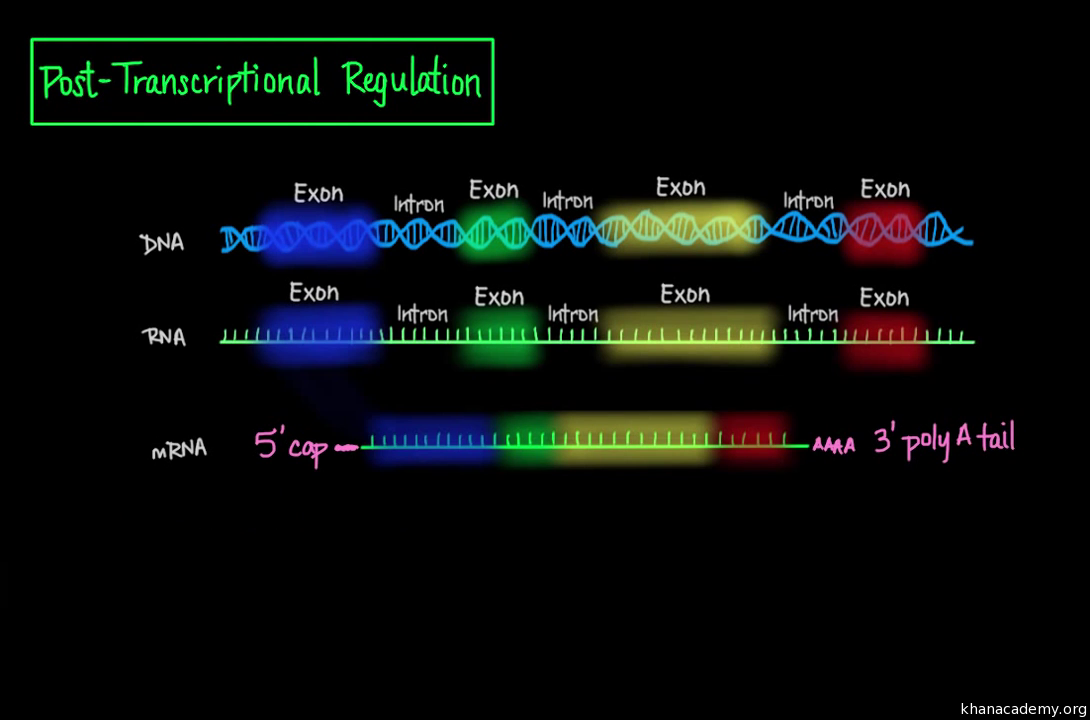
In eukaryotic cells the RNA transcript often contains regions called introns that are removed prior to translation. D Some bases are methylated. RNAs from eukaryotes undergo post-transcriptional modifications including.
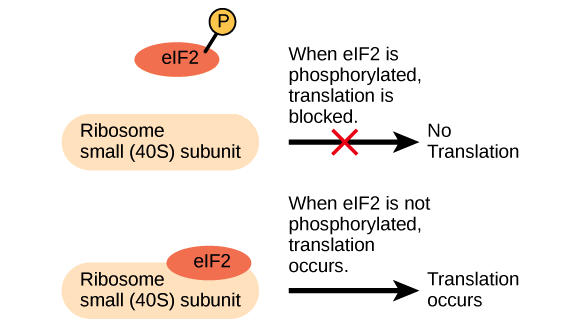
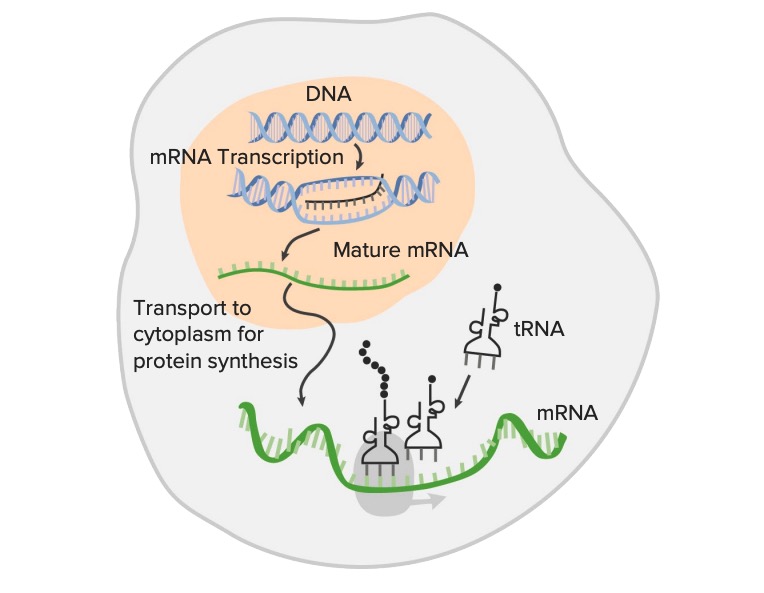
16 - Binding of an RNA binding protein will the. All of the above. The RNA that is synthesized in this process is then transferred to the cells cytoplasm where it is translated into a protein.
Deleting 3 amino acids from a protein chain Mutating a gene Covalently modifying a base in a mRNA sequence Removing a section of a mRNA sequence. All of the above The correct answer is. Post-transcriptional modification of hnRNA involves all of the following except.
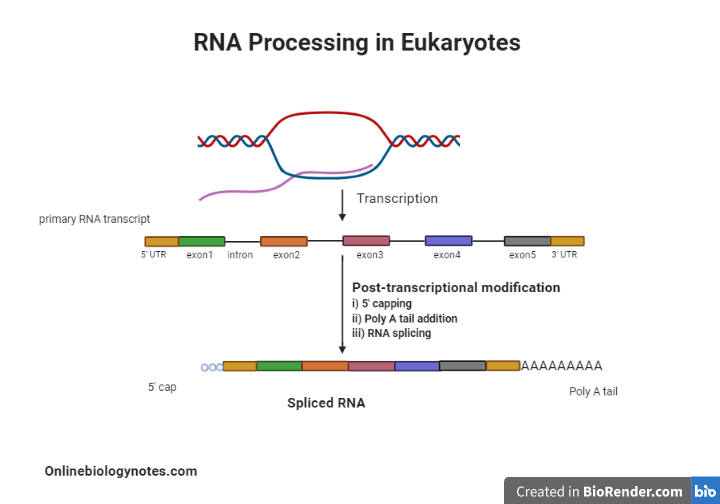
In eukaryotes the primary RNA transcript undergoes structural and chemical changes after transcription to become a mature and functional RNA which is then transported out of the nucleus to perform various functions. A Introns of some tRNA precursors are removed. In this step 7-methylguanosine is added to 5 end of RNA.
Introns are removed from the mRNA. B CCA is added at 3 end. MRNAs in prokaryotes tend to contain many different genes on a single mRNA meaning they are polycystronic.
Post-transcriptional regulation can occur at any stage after transcription including RNA splicing nuclear shuttling and RNA stability. C the excision of introns from mRNA via spliceosome formation. C Mediator Which of the following is not involved in post-transcriptional control.
Capping of eukaryotic mRNAs refers to the addition of 7-Methylguanosine to the 5 end of almost all eukaryotic mRNAs in an unusual 55- triphosphate linkage. Control of RNA shuttling c. Post transcriptional processing of RNA in eukaryotes involves three steps namely capping poly-adenylation and splicing.
Binding of an RNA binding. Post-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an primary RNA transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature functional RNA molecule that can then leave the nucleus and perform any of a variety of different functions in the cell. Addition of a poly A tail.
A poly-A tail is added to the 3 end of the mRNA. A guanine cap is added to the 5 end of the mRNA. In prokaryotes the RNA that is synthesized during DNA transcription is ready for translation into a protein.
B the addition of a 3 poly-adenine tail. All of the following are considered post- transcriptional modifications that occur in the nucleus EXCEPT A 5 capping with methylated guanines. Please log in or register to add a comment.
Post-Transcriptional RNA Processing DNA transcription occurs in a cells nucleus. Which of the following is an example of post- transcriptional control of gene expression. The addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases of DNA gene amplification contributing to cancer the removal of introns and alternative splicing of exons the binding of transcription factors to a promoter.
Which of the following is an example of post-transcriptional control of gene expression. Which of the following are involved in post-transcriptional control. 16 - An unprocessed pre-mRNA has.
-RNA splicing -5 capping -3 polyadenylation -Translation. Which of the following are involved in post. After an RNA molecule has been transcribed but prior to its departure from the nucleus to be translated the RNA is processed and the introns.
Control of RNA stability d. It helps recognition of mRNA by the ribosome during translation process. Capping polyadenylation and splicing.
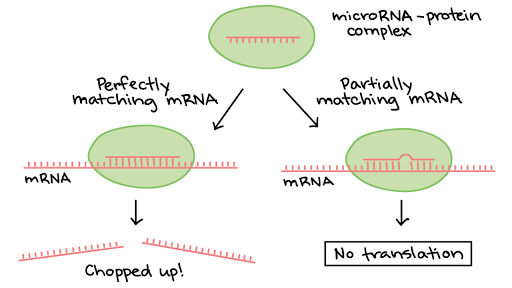
A the addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases of DNA. Post-transcriptional modifications PTMs are processes that facilitate the generation of mature functional RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. D form base pairs with mRNA molecules.
Addition of a methyl. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information serve as. RNA molecules can undergo a number of post transcriptional modifications the most prominent of which is methylation.
All of the following are post-transcriptional processing events that convert eukaryotic pre-mRNA into mature mRNA EXCEPT. Post transcriptional processing of RNA in eukaryotes involves three steps namely capping poly-adenylation and splicing. In this step 7-methylguanosine is added to 5 end of RNA.
Control of RNA splicing b. Controlof RNAsplicing controlof RNA shuttling controlof RNA stability d. Asked Aug 25 2015 in Biology Microbiology by AshleyWY.
These events do not occur in prokaryotes. D Deletion of introns. B the binding of transcription factors to a promoter.
Which of the following statements about post-transcriptional modification are incorrect. C 7-Methylguanosine triphosphate cap is added at 5 end. The regions of RNA that code for protein are called exons.
Which of the following are involved in post transcriptional control. Once RNA is transcribed it must be processed to create a. Different classes of RNA namely mRNA tRNA rRNA ncRNA all can undergo methylation using S.
C Insertion of nucleotides. Post-Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression. B Addition of polyadenylate tail.
9 5 How Genes Are Regulated Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Rna Binding Proteins And Post Transcriptional Gene Regulation Sciencedirect
Regulation After Transcription Article Khan Academy

Regulation After Transcription Article Khan Academy
Rna Post Transcriptional Modification Biology For Majors I
Post Transcriptional Control Of Gene Expression Biology For Majors I
Rna Processing In Eukaryotes Online Biology Notes
Post Transcriptional Regulation Video Khan Academy
Post Transcriptional Modifications Rna Processing Concise Medical Knowledge

Post Transcriptional Regulation Of Gene Expression And Human Disease Abstract Europe Pmc
Regulation After Transcription Article Khan Academy
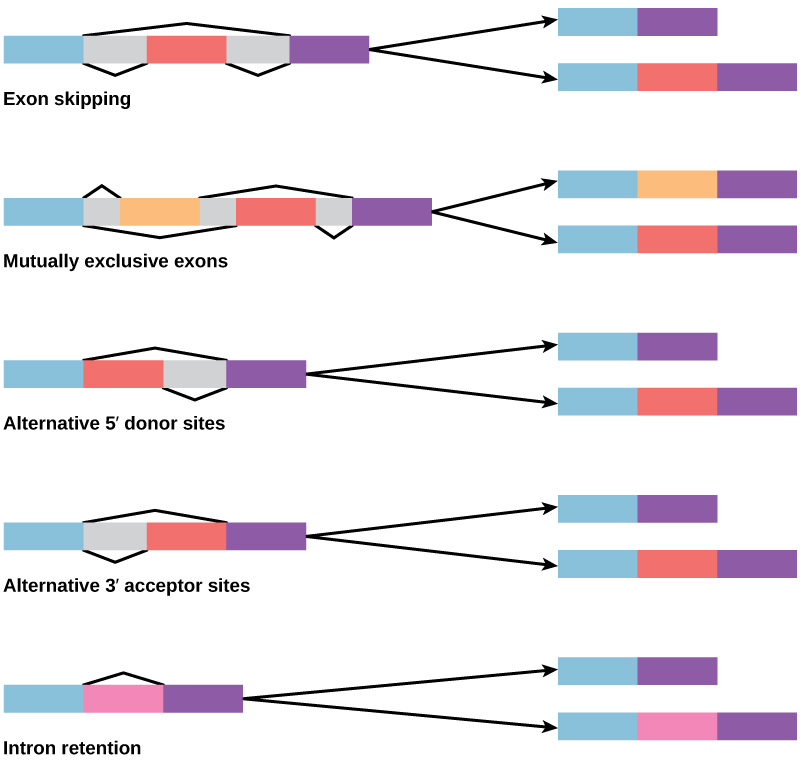
Post Transcriptional Control Of Gene Expression Biology For Majors I

Lesson Explainer Transcription Nagwa

Post Transcriptional Modification Plantlet

Post Transcriptional Control Of Gene Expression Biology For Majors I

Post Transcriptional Modification An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Histone Post Translational Modifications As Potential Therapeutic Targets For Pain Management Trends In Pharmacological Sciences
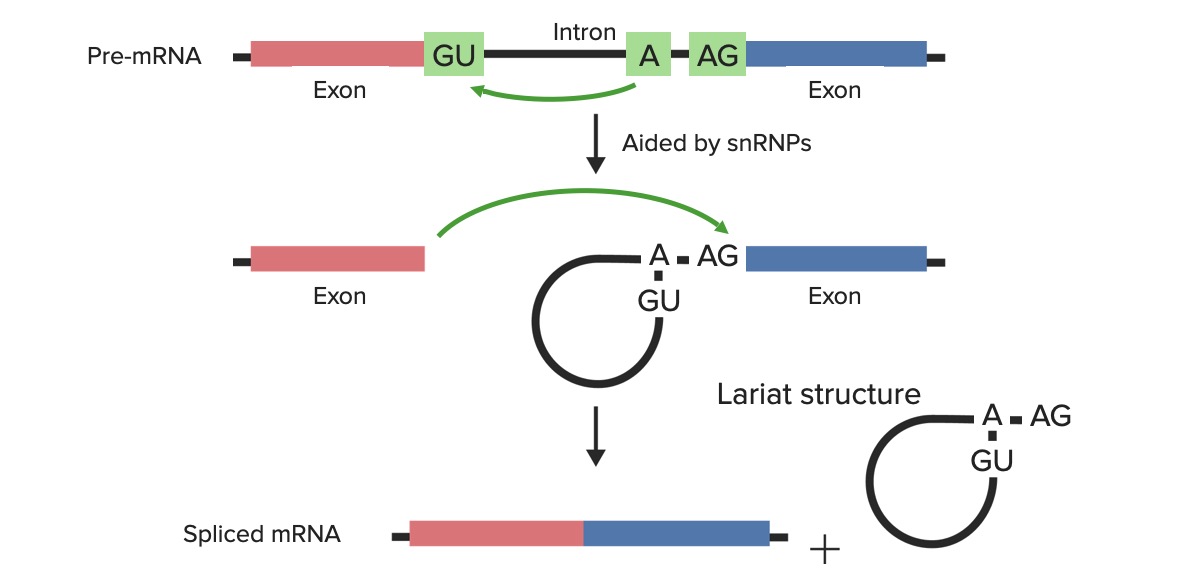
Post Transcriptional Modifications Rna Processing Concise Medical Knowledge

Comments
Post a Comment